Cranes are essential lifting machines widely used in industries such as construction, manufacturing, shipping, and logistics. They come in various types, each designed for specific applications. This article explores the main categories and configurations of cranes, helping you identify the right equipment for your needs.
1. Overhead Bridge Cranes
Overhead bridge cranes feature a bridge girder supported by runways on tracks or directly on a load-bearing surface. They are commonly used in factories, warehouses, and industrial facilities.
1.1 General-Purpose Overhead Crane
Designed for standard industrial environments.
Equipped with hooks, grabs, electromagnetic lifters, or a combination of these.
Note: Excludes cranes with hoists as the lifting mechanism.

1.2 Metallurgical Overhead Crane
Specifically used in metal smelting, casting, rolling, and heat treatment processes.
Built to withstand high temperatures and harsh conditions.
1.3 Explosion-Proof Overhead Crane
Operates safely in explosive gas or dust environments (e.g., chemical plants, oil refineries).
Features spark-resistant and flameproof components.
1.4 Insulated Overhead Crane
Used in electrolytic aluminum, magnesium, lead, zinc, and copper smelting workshops.
Provides insulation against strong electric currents.
2. Gantry Cranes
Gantry cranes have a bridge girder supported by legs that run on tracks or a load-bearing surface. They are ideal for outdoor applications, shipping yards, and large-scale material handling.
2.1 General-Purpose Gantry Crane
Suitable for standard outdoor lifting tasks.
Equipped with hooks, grabs, or electromagnetic lifters.
Note: Excludes hoist-based gantry cranes.

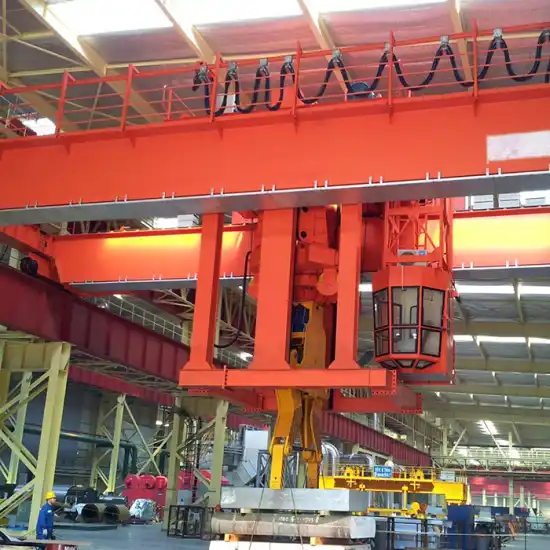
2.2 Shipbuilding Gantry Crane
Designed for shipyards, dry docks, and platforms.
Capable of lifting and rotating large ship sections.
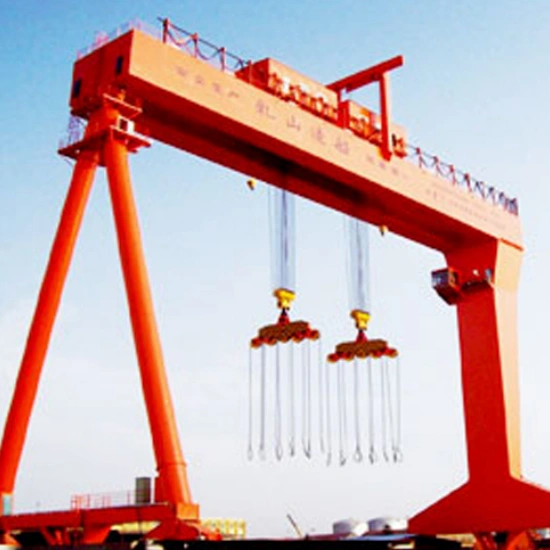
2.3 Ship-to-Shore Container Gantry Crane
Used in ports for loading/unloading containers from ships.
Features an extending boom and specialized container spreader.
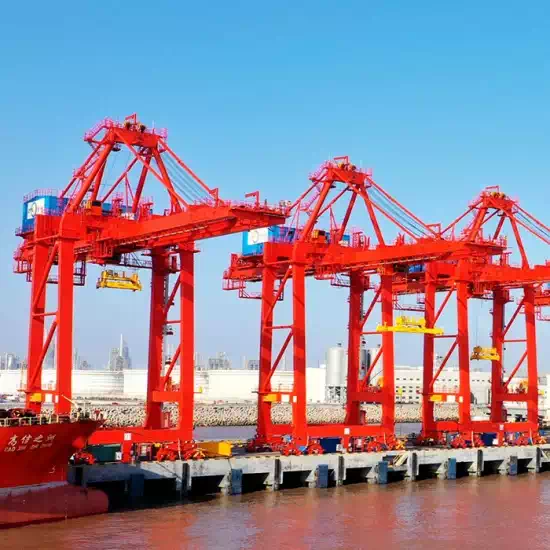

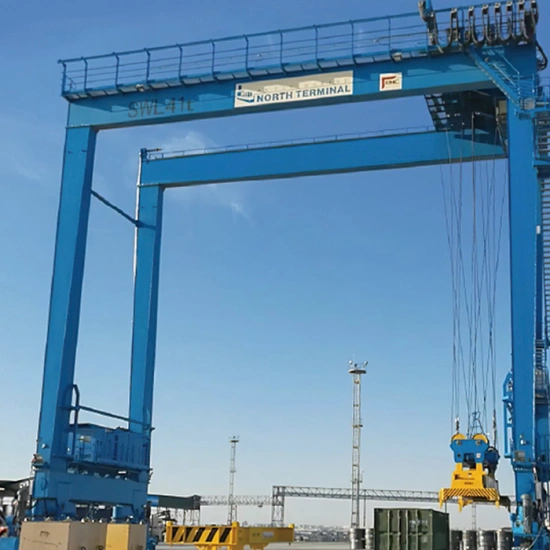
2.4 Rail-Mounted Container Gantry Crane (RMG)
Runs on rails for precise container stacking in terminals.
-
Equipped with a container spreader for efficient handling.
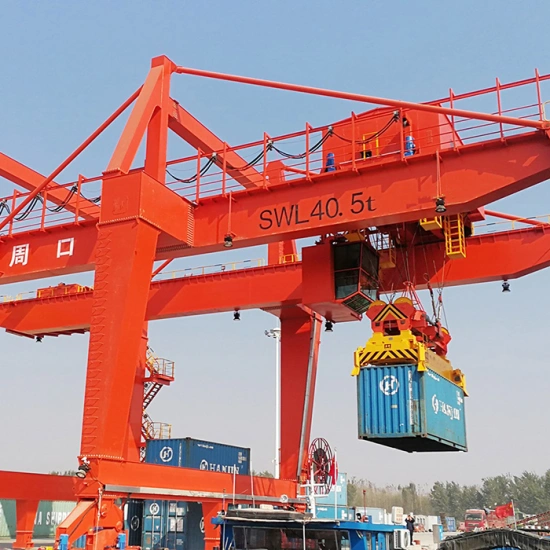

2.5 Rubber-Tired Container Gantry Crane (RTG)
Mobile gantry crane with rubber tires for flexible container movement.
Commonly used in port storage areas.

2.6 Grab Ship Unloader (Bridge-Type Grab Unloader)
Handles bulk materials (e.g., coal, grain) in ports and rail yards.
-
Uses a grab bucket or electromagnetic lifter for rapid unloading.

3. Portal Slewing Cranes
These cranes are mounted on a portal or fixed base, offering stability and rotation capabilities for heavy-duty lifting.
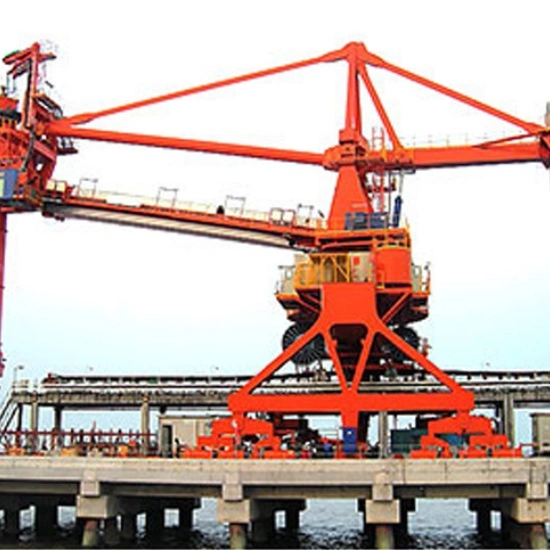
3.1 Portal Slewing Crane
Installed on a gantry structure with a rotating boom.
Used in ports, construction sites, and heavy industries.
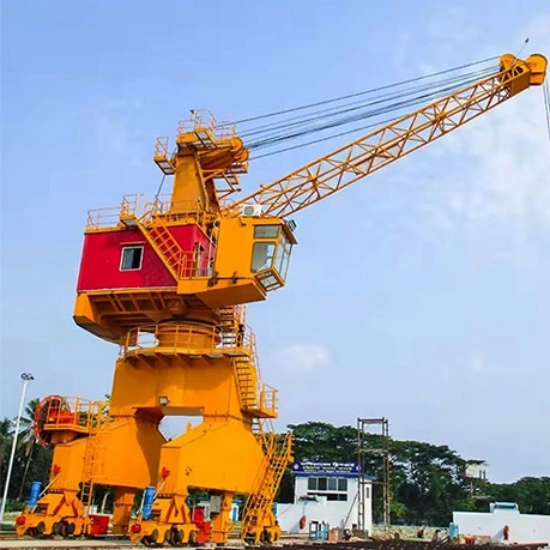

3.2 Fixed Base Crane (Wharf Crane)
Permanently mounted on a foundation (e.g., docks, industrial plants).
Ideal for repetitive lifting operations in a fixed location.
Conclusion
Choosing the right crane depends on the working environment, load requirements, and operational conditions. Whether you need an overhead crane for factory operations, a gantry crane for port logistics, or a slewing crane for heavy lifting, understanding these categories ensures optimal performance and safety.
For more technical insights or customized crane solutions, stay tuned to our blog or contact our experts!