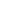What is a Pot Tending Machine?
https://www.zehuacranes.com/POT-Tending-Machine-Crane-for-Electrolytic-Aluminum.html
Pot tending machines are large, automated overhead cranes used in aluminum smelters to perform maintenance on electrolytic cells, or "pots". They are equipped with specialized tools to carry out tasks like replacing worn anodes, breaking crusts on the molten bath, and tapping molten metal. These machines are also known as Pot Cranes, Cell Tending Assemblies, or Anode Changing Machines. Their primary functions include:
Anode replacement: The primary function is replacing worn-out anodes. This involves using tools to remove the old anode's connector, break the crust around the anode, and then fit a new one.
Crust breaking: The machine breaks the solid crust that forms on the surface of the molten bath in the pot.
Metal tapping: Some machines are designed to tap molten metal from the pot.
Alumina feeding: They can add alumina (aluminum oxide) to the pot to maintain stability.
Miscellaneous handling: Pot tending machines can also handle other miscellaneous tasks within the potroom.
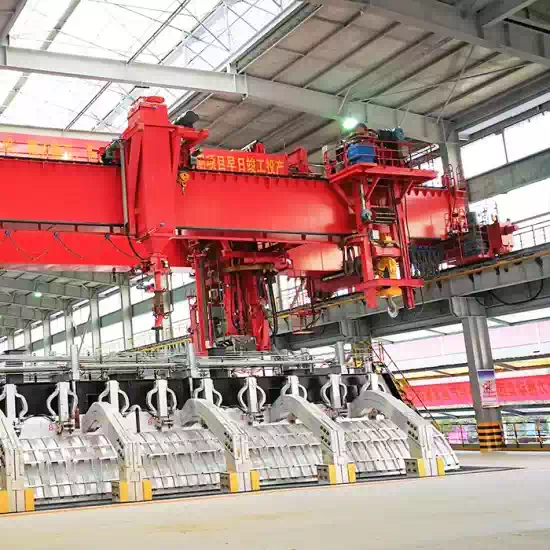

Working Principle and Structural Features of the Electrolytic Aluminum Crane
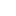
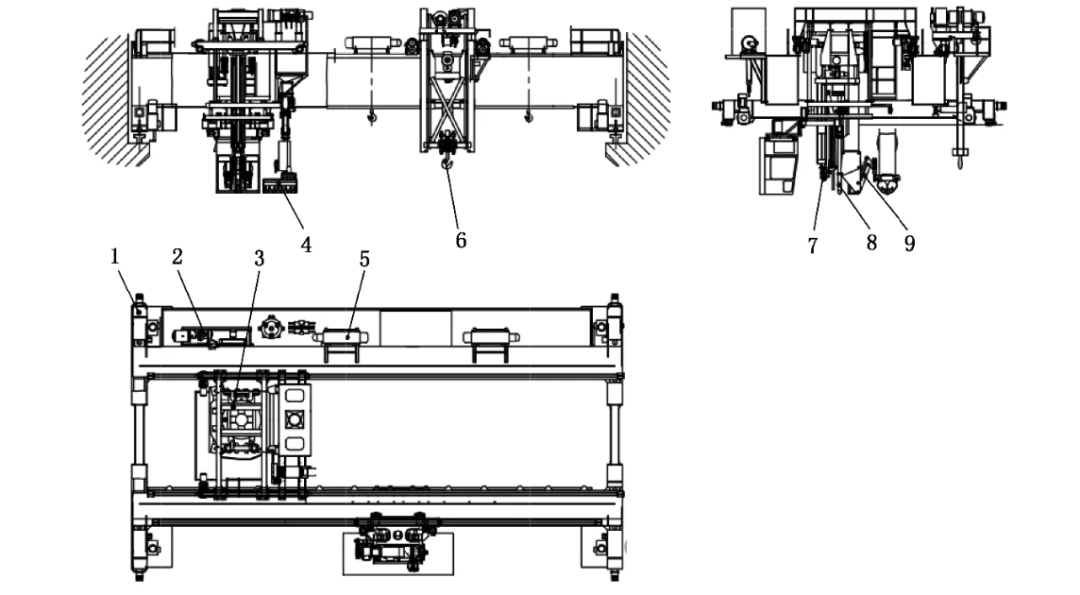
The Pot Tending Machine (PTM) is a specialized, insulated overhead crane designed for the pre-baked anode aluminum electrolysis process. Its bridge is configured with functional components like a tool trolley and a metal tapping trolley. The machine adheres to standards such as the recommended non-ferrous metals industry standard YS/T 7-2020. Key structural components, as illustrated in standards like GB/T 6974.5-2023, include:
Travel Mechanism: The main movement system for the crane.
Air Compressor: Provides power for various pneumatic tools.
Tool Trolley: A central unit housing multiple maintenance tools.
Slag Removal Device: Cleans residual materials from the pots.
Auxiliary Hoisting Device: Assists with secondary lifting tasks.
Metal Tapping Trolley: Specifically designed for tapping molten aluminum.
Anode Replacement Device: The core mechanism for swapping anodes.
Feeding System: Delivers alumina into the electrolytic cell.
Crust Breaking Mechanism: Used to break the solidified surface crust.
This integrated design allows the PTM to perform all essential potroom tasks efficiently and reliably from a single platform.
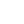
Core Competitive Advantages of the Pot Tending Machine
The Pot Tending Machine offers several key advantages that make it indispensable in modern aluminum production:
Enhanced Operational Safety: By automating hazardous tasks performed in extreme heat and close to molten metal, PTMs significantly reduce the risk of workplace accidents and exposure to harmful fumes for personnel.
Maximized Productivity and Uptime: These machines enable faster and more precise pot servicing compared to manual or semi-mechanized methods. This leads to shorter cycle times, increased potline availability, and higher overall production output.
Superior Process Control and Consistency: Automated PTMs execute tasks with high repeatability, ensuring that anode changes, crust breaking, and alumina feeding are performed uniformly. This consistency is crucial for maintaining the delicate thermal and chemical balance of the electrolytic cells, which directly impacts metal quality and energy consumption.
Improved Cost-Efficiency: While representing a significant capital investment, PTMs lower long-term operating costs through reduced labor requirements, minimized material waste, and optimized energy use per ton of aluminum produced.
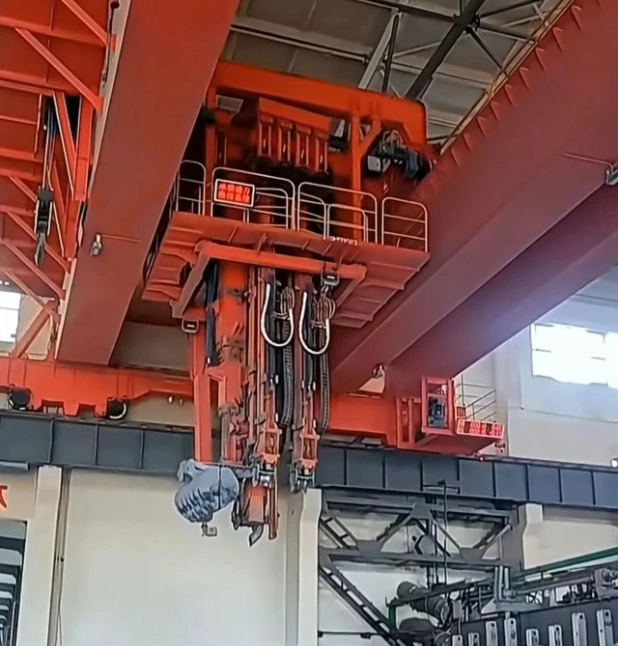
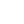
Versatile Application Scenarios for the Pot Tending Machine for Electrolytic Aluminum
The functionality of the Pot Tending Machine extends across the entire potroom operation, making it a versatile workhorse:
Routine Anode Cycle Management: Its primary role is the continuous, scheduled replacement of consumed carbon anodes throughout the potline.
Molten Metal Harvesting: Equipped with a tapping trolley, the PTM is used to siphon molten aluminum from the pots into crucibles for transport to casting facilities.
Cell Feeding and Crust Management: The machine regularly breaks the hardened bath crust and feeds fresh alumina into the pot, maintaining the electrolysis process.
Pot Maintenance and Repair: PTMs are crucial for larger-scale pot maintenance, including lining repairs, busbar work, and full cell relining, using their powerful hoists and precise positioning.
Slag and Skimming Removal: The integrated tools allow for the removal of excess bath material and impurities from the pot surface.
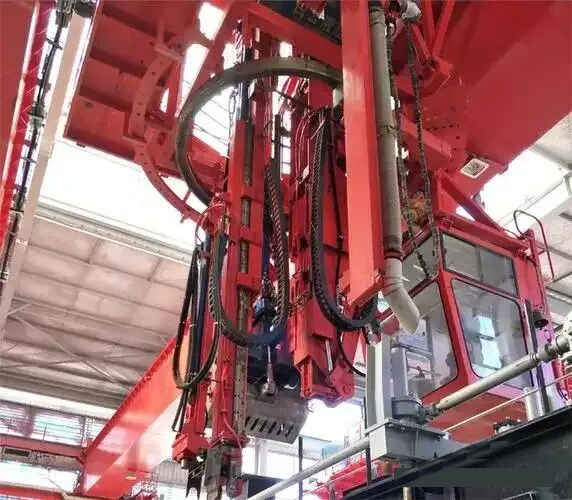

Technological Innovation and Future Outlook for Pot Tending Machines
The future of Pot Tending Machines is being shaped by rapid technological advancements aimed at creating "smart" potrooms.
Integration of Industry 4.0 and IoT: Modern PTMs are increasingly equipped with sensors and data acquisition systems. They collect real-time data on pot conditions, anode status, and machine performance, enabling predictive maintenance and data-driven process optimization.
Advanced Automation and Robotics: The next generation of PTMs features higher levels of autonomy. This includes automated navigation, robotic tool changing, and vision systems for precise anode positioning and crust breaking, further reducing human intervention.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI algorithms can analyze operational data to optimize task sequences, predict anode failures before they occur, and automatically adjust operational parameters for peak efficiency and energy savings.
Enhanced Energy Efficiency: Future designs will focus on reducing the machine's own energy consumption through regenerative drives, lighter materials, and more efficient hydraulic and pneumatic systems.
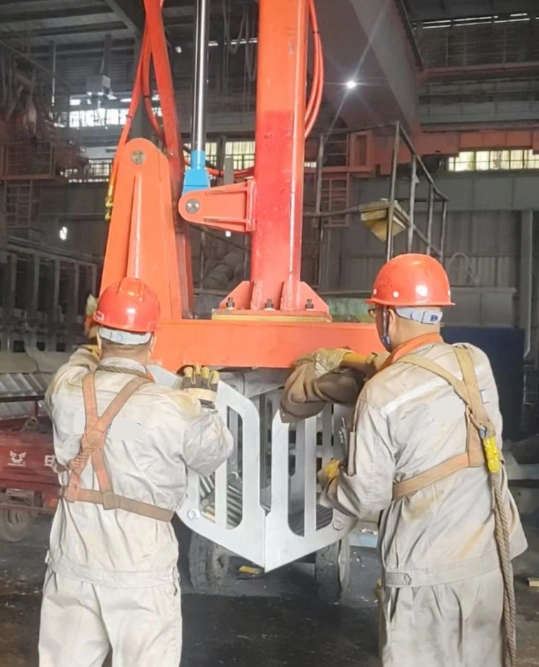

In conclusion, the Pot Tending Machine is evolving from a basic maintenance crane into a central, intelligent data hub and automation platform, poised to drive the aluminum industry towards unprecedented levels of safety, efficiency, and sustainability.
HENAN ZEHUA HEAVY INDUSTRY EQUIPMENT CO., LTD
Email: sale@zehuacranes.com
Website: [https://www.zehuacranes.com/]
Whatsapp:86-19562739544